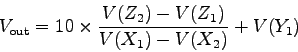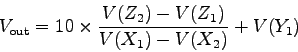


Next: Active filters and tuned amplifiers
Up: Analog multiplier
Previous: Analog multiplier
- To obtain division, connect the multiplier output to the
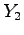 input. Now
input. Now
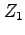 is no longer connected to the output, and
is no longer connected to the output, and 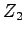 is no longer grounded.
In this configuration:
is no longer grounded.
In this configuration:
Measure 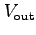 for several values of
for several values of 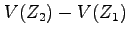 and
and
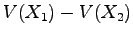 .
For simplicity, you may want to ground
.
For simplicity, you may want to ground 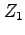 ,
, 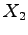 , and
, and 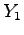 . Make sure you
keep
. Make sure you
keep 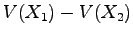 positive (see the spec sheets of AD534).
positive (see the spec sheets of AD534).
- The output limits of AD534 are
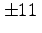 V.
Calculate and plot the minimum value
for
V.
Calculate and plot the minimum value
for 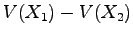 as a function of
as a function of 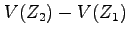 over the
over the 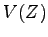 range of
range of 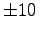 V.
V.
For info, write to: physics@brocku.ca
Last revised: 2007-01-05